BPSim standard specification for parameterizing your model: definition and benefits
Written by Teresa Montrone
3 March 2025 · 5 min read

In the last few months, we've been busy working on introducing Business Process Simulation in Cardanit. Cardanit began as an intuitive editor for modeling your business processes, but now you can actually bring those models to life by simulating them. This allows you to validate and improve your processes as explained in a previous blog post. Before you can really start simulating your business processes, there are a few necessary steps to take care of. One of them is parameterization, and we've opted to use the BPSim standard specification for this. In this blog post, we'll get into the details of the BPSim standard specification and explain why we think it's the best choice for you.
Business process simulation in the BPM lifecycle
In another blog post, we delved into the five steps of the Business Process Management (BPM) lifecycle: Design, Modeling, Execution, Monitoring, and Optimization. Integrating business process simulation into this cycle is crucial. Process simulation enables you to effectively execute, monitor, and optimize your business processes.
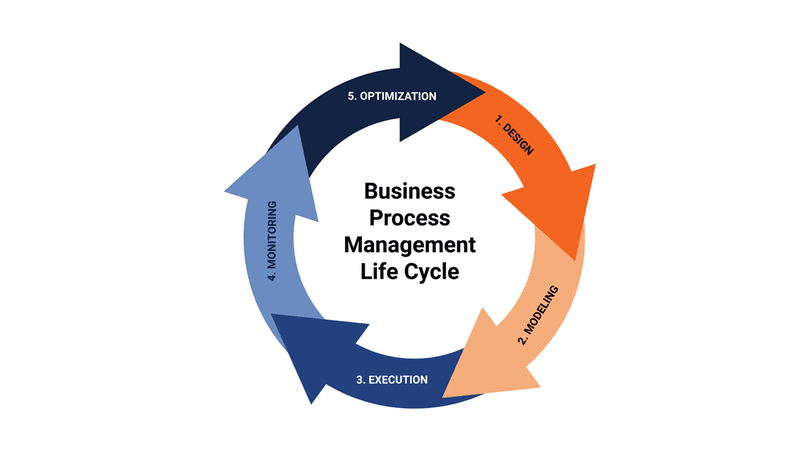
When it comes to using business process simulation, there are some important steps to keep in mind. Design and modeling are also the initial steps for business simulation. But before diving into animating your process, it's essential to gather real data to accurately reflect your business operations in your model. Then the parameterization of your model with this data is essential for an effective business simulation, ensuring that you obtain the most accurate and useful results. BPSim is the standard that we decided to incorporate for parameterizing your business process models and this is how you get a reliable digital twin of your business model.
BPSim standard specification for parameterizing your model
BPSim is an abbreviation for Business Process Simulation Standard, which allows models to be captured in BPMN or XPDL.
This specification includes
- a meta-model, which is a computer-interpretable representation
- an interchange format, to facilitate the storage and transfer of data between different tools.
The BPSim meta-model uses the Unified Modeling Language (UML), and the interchange format is defined using an XML Schema Definition (XSD). This standard outlines the parameterization and interchange of process analysis to support pre-execution and post-execution optimization of process models. It helps capture both inputs and outputs of process analysis, including estimated and historical execution values.
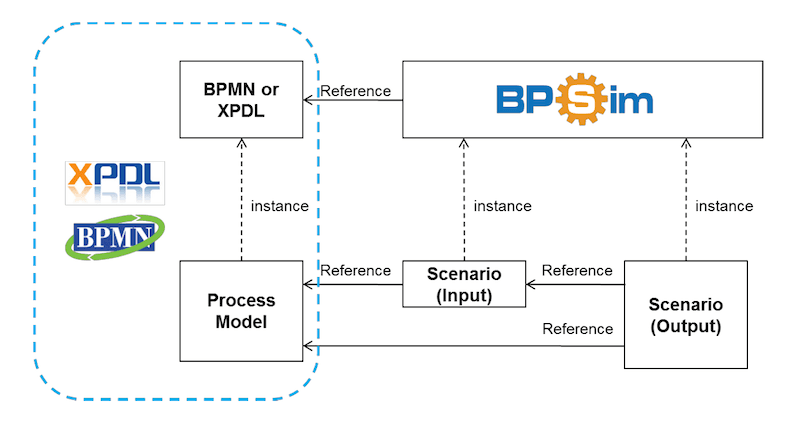
How to explore all the aspects of process analysis with BPSim
BPSim helps to explore all aspects of the process analysis. This includes scenarios, which help capture input parameters, results, and historical data from real-world execution of the business process model. When we talk about scenarios, we’re referring to a collection of element parameters. Each of these parameters references to a specific element of the business process model. In turn, each element of the business process model can have multiple element parameters. Here’s a list of each element parameter and what they specify:
- Time Parameters, for time for a business process element
- Control Parameters, for control flow of a business specific element
- Resource Parameters, for the resources of a business process element
- Cost Parameters, for the cost of a business process element
- Property Parameters, for global property of a business process element
- Priority Parameters, for the priority of a business process element
Each parameter can be assigned to different elements. For instance, time parameters can be assigned to tasks or all other activities that don’t include lower-levels. The type of these parameters can be boolean, constants, distributions, given expressions, or calendar. Each parameter has a specific meaning that is explained by the standard specification. For example, the processing time for a task is the time actually spent doing the work at hand.
When it comes to setting these parameters, Cardanit offers an intuitive interface for assigning them to specific business process elements, that is all explained in our documentation.
BPSim gives the results in a standard way
Cardanit enables you to automatically access all requested results in the simulation results table. Each output parameter in the results table corresponds to a specific output parameter of the specification.
Cardanit offers a convenient way for you to effortlessly access all the results you need in the simulation results table. Every output parameter in the results table is directly linked to a specific output parameter of the specification. This makes it easy for you to find the information you're looking for quickly and efficiently.
The benefits of using BPSim
Let's explore why we chose to adopt BPSim. The reason behind this decision is the universal acceptance and understanding of BPSim as a standard in the business process world. Instead of creating something brand new, we opted to utilize a standard that perfectly complements BPMN, which is the standard adopted by Cardanit. Indeed, BPSim was specifically designed to work alongside existing business process modeling standards, such as BPMN 2.0. Its aim is to prevent duplicating process model information already provided by this standard and ensure proper extension mechanisms for interchange within BPMN, XPDL or standalone XML files.
This standard ensures that the XML file is easily comprehensible and well-structured in useful classes. BPSim's widespread use and value make it convenient for you to verify and validate your work.
Cardanit allows you to import an XML containing all parameters, and once imported, all parameters are automatically displayed in our interface. When you simulate this model, you can download an XML file with the outputs added in the style required by the specification. Thus, Cardanit enables you to read and create XML files that are understandable by anyone familiar with BPMN and BPSim.
Close the business process management cycle
Once you've set the parameters for your model, it's time to run it! Keep a close eye on the results and take time to analyze them. This is your chance to see if your model and parameters are the perfect fit. If not, just make some modifications to parameters or model and run it again until you find that sweet spot. This is how you optimize your business model and close the lifecycle of business process management.
Further reading
Process validation: how Process Simulation helps verify BPMN models
The five steps of the Business Process Management lifecycle
Simulation in Cardanit documentation
Teresa Montrone joined ESTECO in 2013 for a PhD in Mathematics in collaboration with the University of Salento. She started belonging to the Numerical Method Group as researcher in optimization, response surface and Design of Experiments. After 8 years she took on the researcher and developer roles in the team developing Cardanit. She’s also been involved in research projects in the field of railways and transportation, applying her expertise in combinatorial methods, optimization and business process simulation. In 2024, Teresa got promoted to Project Manager, coordinating Cardanit development.
Teresa Montrone joined ESTECO in 2013 for a PhD in Mathematics in collaboration with the University of Salento. She started belonging to the Numerical Method Group as researcher in optimization, response surface and Design of Experiments. After 8 years she took on the researcher and developer roles in the team developing Cardanit. She’s also been involved in research projects in the field of railways and transportation, applying her expertise in combinatorial methods, optimization and business process simulation. In 2024, Teresa got promoted to Project Manager, coordinating Cardanit development.
A business is only as efficient as its processes. What are you waiting to improve yours?
